The Role of Fiber in a Healthy Gut
Understanding Fiber’s Role in Gut Health
Fiber is a vital component of our diet that plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy gut. It is classified into two categories: soluble and insoluble fiber, both of which offer distinct benefits for digestive health. Soluble fiber, found in foods like oats and beans, dissolves in water and helps to regulate blood sugar levels, while insoluble fiber, present in whole grains and vegetables, adds bulk to stool and facilitates its passage through the digestive tract. Incorporating a mix of both types of fiber can enhance overall gut health.
The Benefits of Soluble Fiber
Soluble fiber is known for its ability to improve gut health by feeding beneficial gut bacteria. These bacteria ferment soluble fiber, producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) which have numerous health benefits, including reduced inflammation and improved immunity. Foods rich in soluble fiber include
- Oats
- Barley
- Fruits like apples and citrus
- Beans and lentils
By including these foods in your diet, you can promote the growth of good bacteria, which is essential for a healthy digestive system.
Insoluble Fiber and Digestive Health
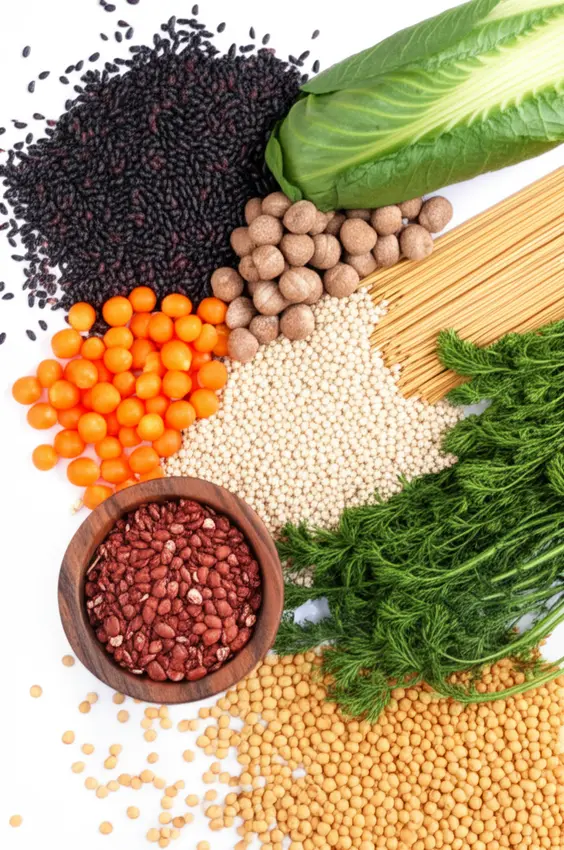
In contrast, insoluble fiber plays a pivotal role in adding bulk to the stool, which helps prevent constipation and promotes regular bowel movements. It also aids in moving food through the digestive system, making it a key player in preventing digestive disorders such as diverticulitis. Foods high in insoluble fiber include
- Whole wheat
- Brown rice
- Nuts and seeds
- Vegetables like carrots and celery
Incorporating these foods can make a significant difference in your digestive health.
How Fiber Affects Gut Microbiota
Fiber serves as a prebiotic, which means it provides nourishment for the beneficial microorganisms in your gut. A healthy gut microbiota is essential for effective digestion, nutrient absorption, and a strong immune system. Research shows that a diverse diet rich in fiber can lead to a more diverse microbiome, which is linked to better health outcomes. To achieve this, aim to introduce a variety of fiber sources into your meals, thereby creating a thriving environment for your gut bacteria!
The Importance of Increasing Fiber Intake Gradually
When increasing fiber in your diet, it’s essential to do so gradually. This approach helps your digestive system adjust without discomfort such as bloating or gas. Start by adding small amounts of fiber-rich foods to your meals and gradually increase the quantity. Also, remember to drink plenty of water—I recommend at least 8 glasses a day—as this aids in the digestion of fiber and helps prevent constipation.
In Conclusion: A Journey to Gut Health
Embracing a fiber-rich diet not only improves gut health but also contributes to overall well-being. Begin by understanding the different types of fiber and their benefits, and make a conscious effort to include both soluble and insoluble fiber in your meals. Your gut will thank you for the nourishing benefits that a fiber-rich diet provides, leading to a happier, healthier YOU!